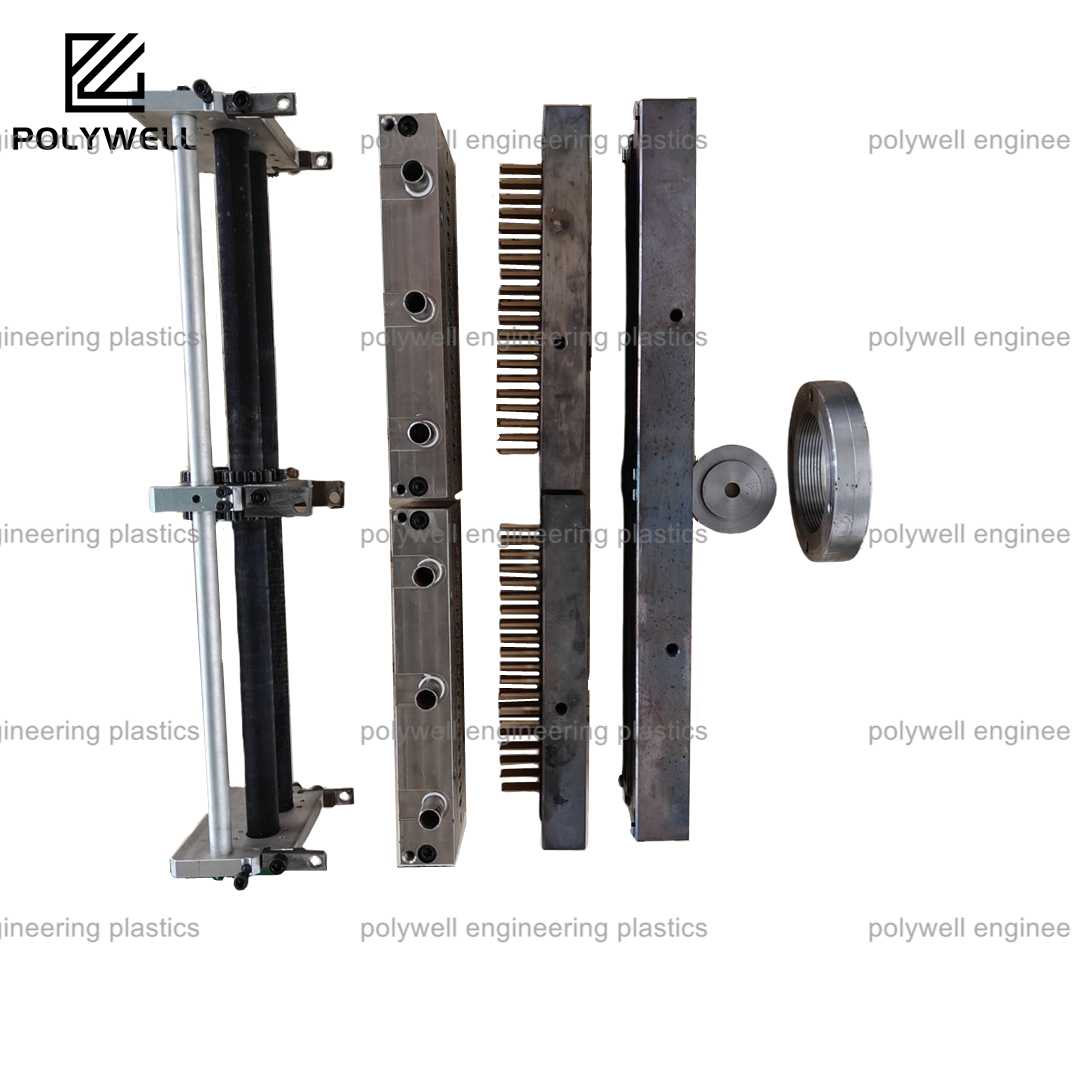
Mold design for injection molding is a specialized engineering discipline focused on creating tooling systems that transform molten plastic into precise, repeatable components. The process requires deep understanding of polymer behavior, thermal dynamics, and mechanical engineering principles applied within the constraints of high-volume manufacturing. Fundamental design considerations begin with determining the optimal mold type—two-plate for simplicity, three-plate for automated runner separation, or stack molds for increased capacity. The parting line establishment is crucial, affecting both part aesthetics and mold functionality. Cavity and core design must account for material shrinkage, incorporating appropriate scale factors to achieve final part dimensions. Feeding system engineering encompasses runner layout (naturally balanced or geometrically balanced), gate type selection (edge, submarine, fan, or diaphragm), and sprue design, with decisions between cold runner and hot runner systems significantly impacting material efficiency and cycle time. Cooling system design employs strategically placed channels to extract heat uniformly, preventing warpage and reducing cycle times. Ejection system engineering ensures reliable part removal through pins, sleeves, blades, or stripper plates positioned to apply force without damaging the part. Complex part geometries require additional mechanisms including lifters for undercuts, sliders for side features, and unscrewing devices for threaded components. Venting design prevents air entrapment that causes burns or short shots, while alignment systems maintain precision throughout the molding cycle. Modern mold design utilizes advanced simulation software to predict filling patterns, cooling efficiency, and structural stresses, enabling optimization before costly tool fabrication. The resulting mold design represents a balance between technical performance, manufacturing efficiency, maintenance requirements, and economic considerations, delivering a robust manufacturing system capable of producing high-quality components consistently.