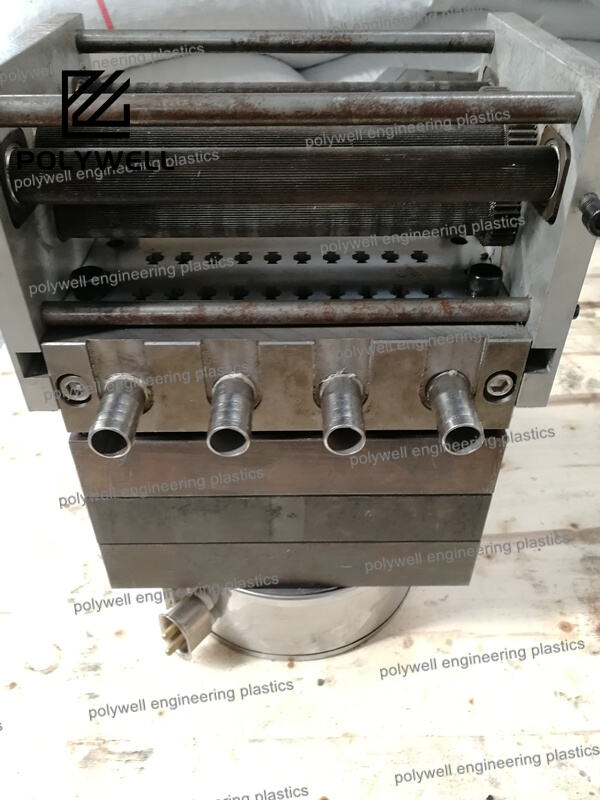
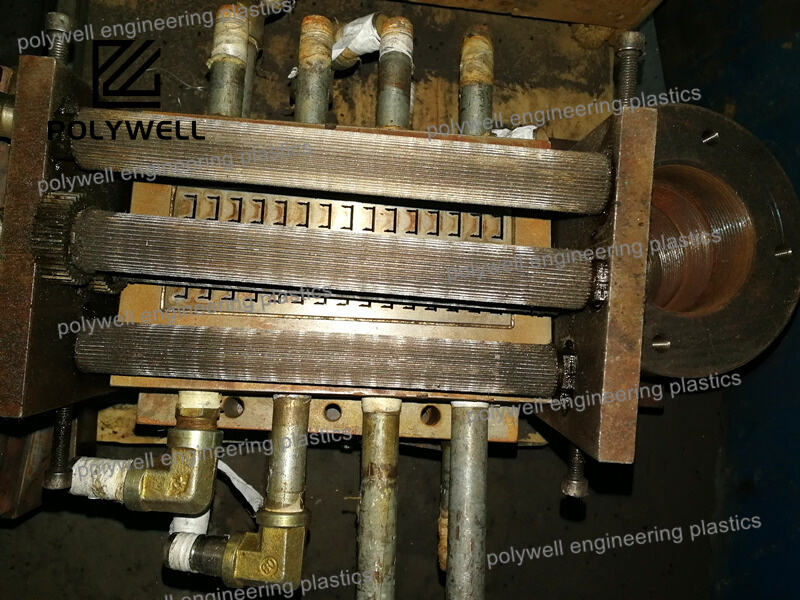
Mold injection design, more accurately described as injection mold design, is the comprehensive engineering process that creates the tooling system for plastic injection molding. This multidisciplinary field combines mechanical engineering, materials science, thermal dynamics, and manufacturing principles to develop molds that produce plastic parts efficiently, consistently, and economically. The design process begins with thorough analysis of the part design, identifying potential manufacturing challenges and opportunities for optimization. Critical design elements include the cavity and core system that forms the part geometry, the feeding system that delivers molten plastic to the cavity, the cooling system that regulates mold temperature, the ejection system that removes finished parts, and the structural framework that supports all components under high injection pressures. Advanced molds incorporate complex mechanisms such as hydraulic or pneumatic side-actions for undercuts, unscrewing devices for threaded parts, and stack molds for increased production capacity. Material selection for mold components balances factors including wear resistance, polishability, thermal conductivity, and cost, with common choices ranging from P20 steel for moderate production to hardened steels like H13 for abrasive materials or high-volume applications. Modern injection mold design heavily relies on sophisticated software tools for 3D modeling, finite element analysis, and molding simulation, allowing engineers to predict and address potential issues before tool fabrication. The design must also consider practical manufacturing concerns such as ease of maintenance, repairability, and compatibility with standard molding machines. Successful injection mold design delivers a robust manufacturing system that operates reliably over hundreds of thousands of cycles while producing parts that meet precise dimensional, cosmetic, and performance specifications.