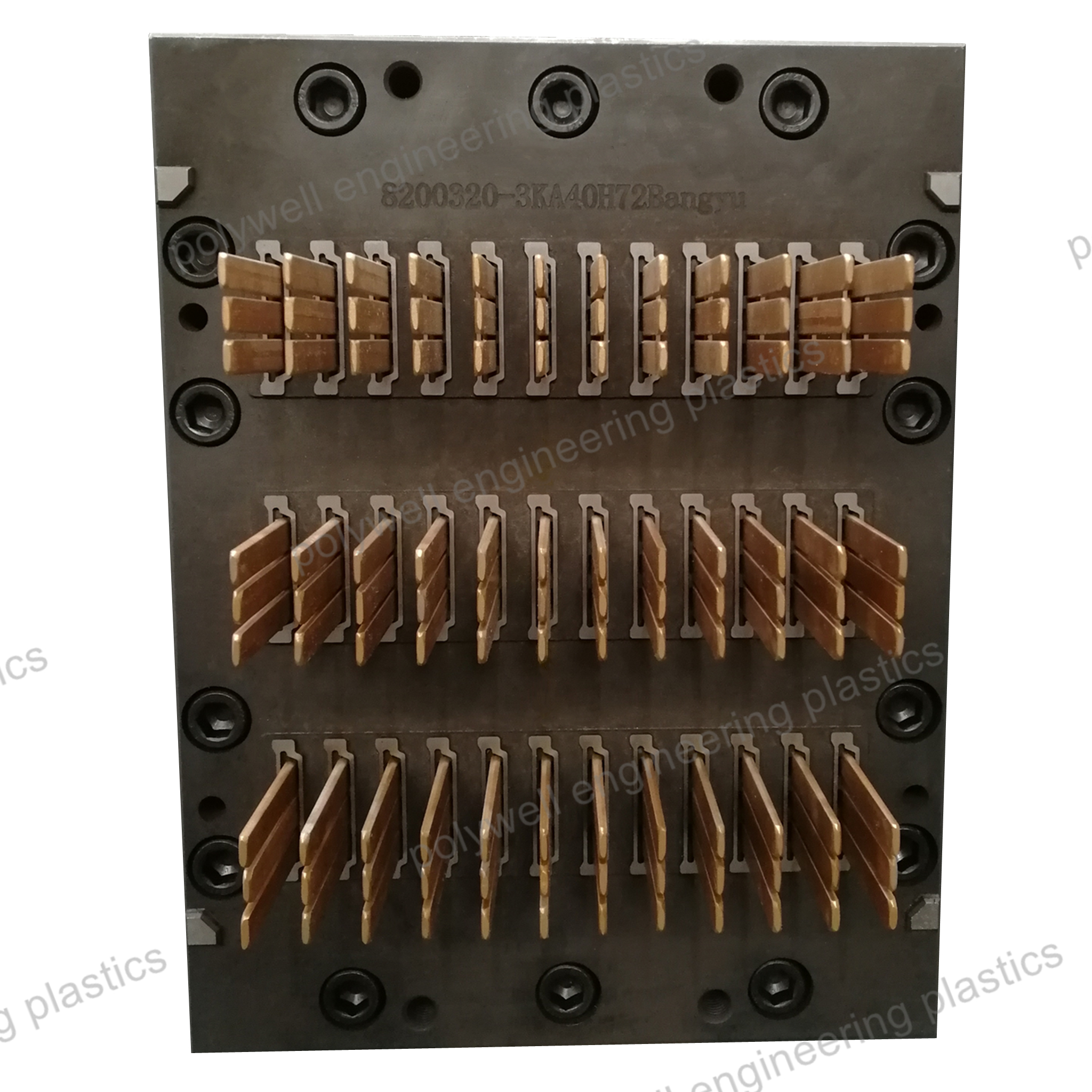
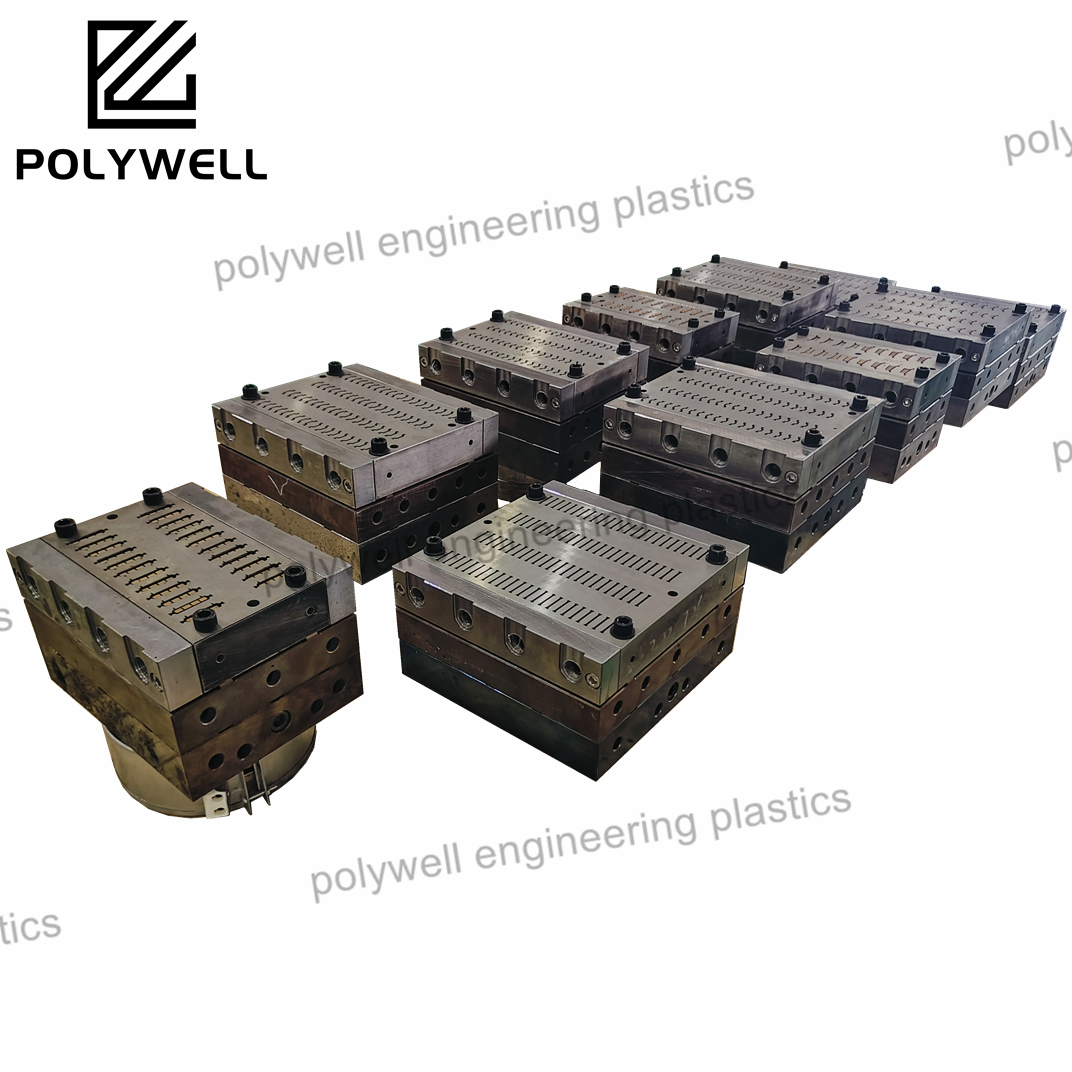
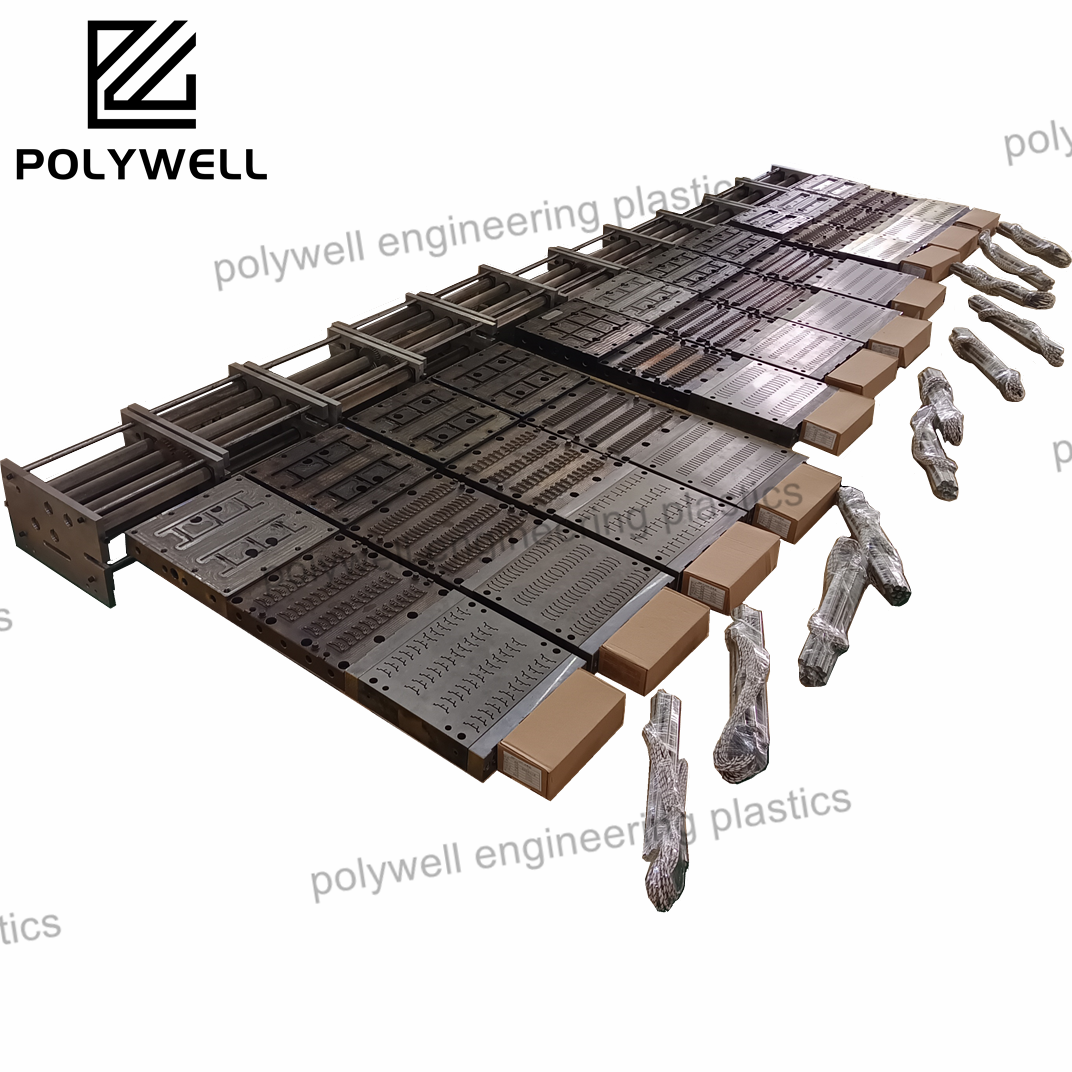
Injection design, in the context of plastic injection molding, encompasses the comprehensive engineering process of developing components specifically optimized for the injection molding manufacturing method. This specialized field integrates material science, mechanical engineering, and manufacturing principles to create parts that are functional, cost-effective, and manufacturable. The process begins with establishing appropriate wall thickness, which must remain uniform throughout the part to prevent sink marks, warpage, and internal stresses. Draft angles are incorporated on all surfaces parallel to the mold opening direction to facilitate clean part ejection without damage. Structural elements like ribs, gussets, and bosses are strategically designed to enhance stiffness without creating thick sections, with careful attention to their proportions relative to adjacent walls. Corner transitions employ generous radii to distribute stress concentrations and improve material flow during molding. Material selection is fundamental, with choices based on mechanical requirements, environmental exposure, regulatory compliance, and cost considerations. The design must also account for shrinkage behavior, which varies significantly between different polymer types and is influenced by fiber orientation in reinforced materials. Gate locations are strategically planned to control weld line positions, minimize flow length, and optimize fiber orientation for structural performance. Advanced injection design incorporates design for assembly (DFA) principles, optimizing features for snap-fits, ultrasonic welding, press fits, or threaded fasteners. Modern practice heavily relies on simulation tools to predict mold filling patterns, cooling efficiency, warpage tendencies, and structural performance under load. The iterative design process balances aesthetic requirements with functional performance, often requiring compromises between ideal geometry and manufacturing practicality. Successful injection design delivers components that not only meet performance specifications but also optimize production economics through reduced cycle times, minimized material usage, and simplified assembly operations, while adhering to global standards for quality and safety.