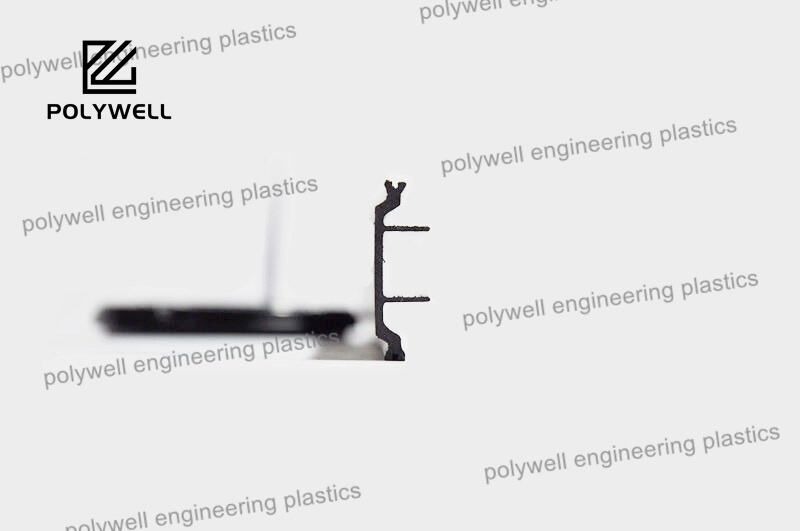
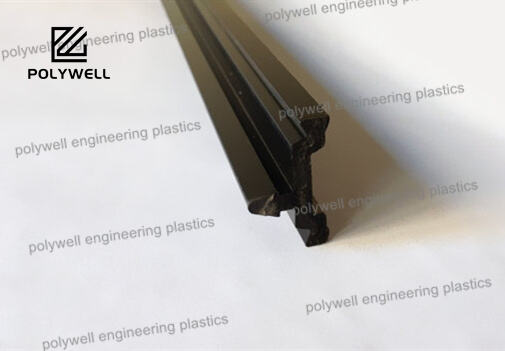
Thermal and acoustic insulation represents a dual-function material category engineered to simultaneously manage heat transfer and sound propagation in built environments and industrial applications. These advanced composite materials address two fundamental physics principles: reducing conductive, convective, and radiant heat flow while absorbing, blocking, or damping sound energy. The material science behind these insulators often involves complex matrices containing fibrous structures (fiberglass, mineral wool), cellular foams (polyurethane, polystyrene), or viscoelastic compounds that provide both thermal resistance and sound absorption. Thermal performance is quantified by R-value (imperial) or lambda-value (metric), indicating resistance to heat flow, while acoustic effectiveness is measured through Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC), Sound Transmission Class (STC), and Impact Insulation Class (IIC) ratings. Advanced products may incorporate mass-loaded vinyl barriers for low-frequency noise suppression alongside aerogel-enhanced layers for maximum thermal resistance in constrained spaces. Manufacturing processes precisely control material density, porosity, and layer composition to optimize both functionalities. Applications span building envelopes (walls, roofs, floors), mechanical equipment enclosures, automotive compartments, and industrial machinery housing. Installation considerations include continuous coverage to prevent thermal bridging and proper sealing to eliminate acoustic flanking paths. These systems contribute significantly to energy conservation, reducing heating and cooling loads while enhancing occupant comfort through noise reduction. Modern developments focus on sustainable materials with recycled content, low VOC emissions, and end-of-life recyclability. Performance validation through standardized testing (ASTM, ISO, EN) ensures compliance with international building codes and green certification programs. The integration of thermal and acoustic insulation represents a holistic approach to environmental control, particularly valuable in urban settings where energy efficiency and noise pollution mitigation are equally prioritized.