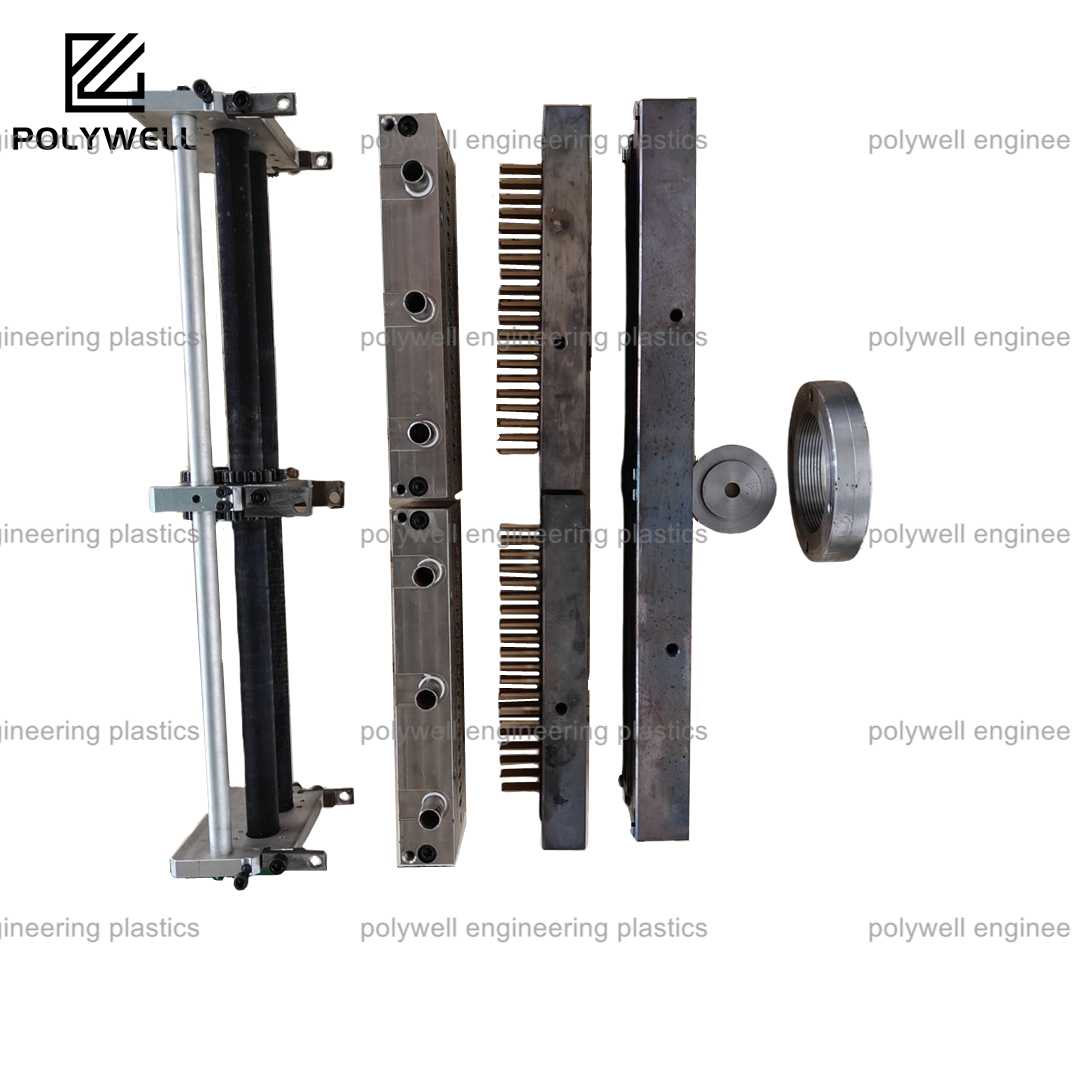
Silicone mold design focuses on creating durable, flexible molds primarily used for casting rubber, polyurethane, or other elastomers in applications ranging from medical devices to consumer products. This process leverages silicone's high thermal stability, chemical resistance, and low shrinkage properties, which are essential for producing precise, high-quality parts. Key design considerations include selecting the appropriate silicone grade (e.g., platinum-cure or tin-cure) based on factors like cure time, flexibility, and compatibility with casting materials. Mold geometry must account for undercuts and complex shapes, often incorporating draft angles and vents to facilitate air escape and prevent defects like bubbles. The use of 3D printing or CNC machining for master patterns enables rapid prototyping and accuracy in mold cavities. In injection molding contexts, silicone molds require robust support structures and gating systems, such as diaphragm gates, to ensure even material flow and minimize turbulence. Cooling systems are less critical than in thermoplastic molding but still important for controlling cure rates and cycle times. Designers must also address demolding techniques, using release agents or split molds to avoid damage, and consider environmental factors like humidity that affect silicone performance. Overall, silicone mold design demands a balance between material science, mechanical engineering, and process optimization to achieve repeatability and cost-effectiveness in various industrial sectors.