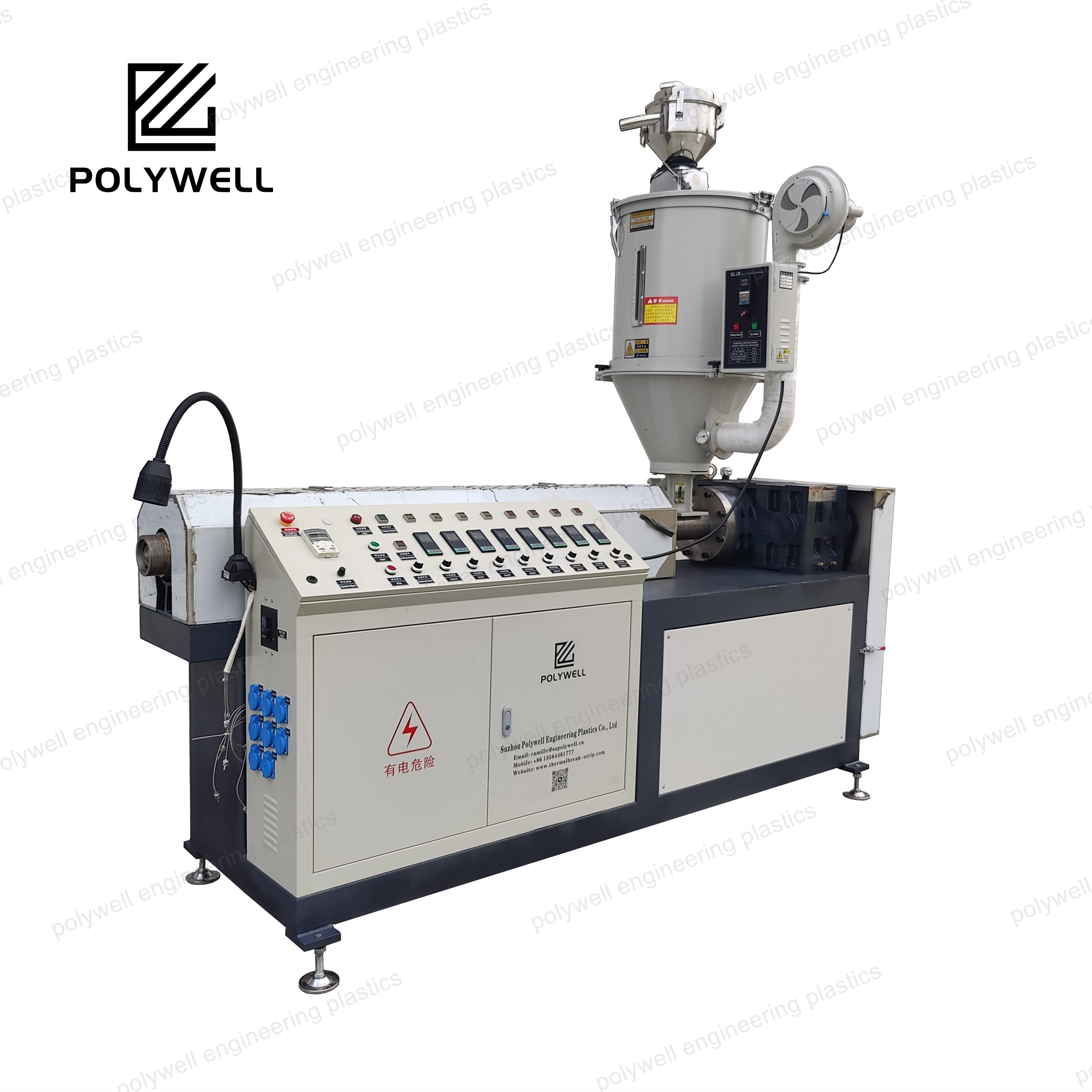
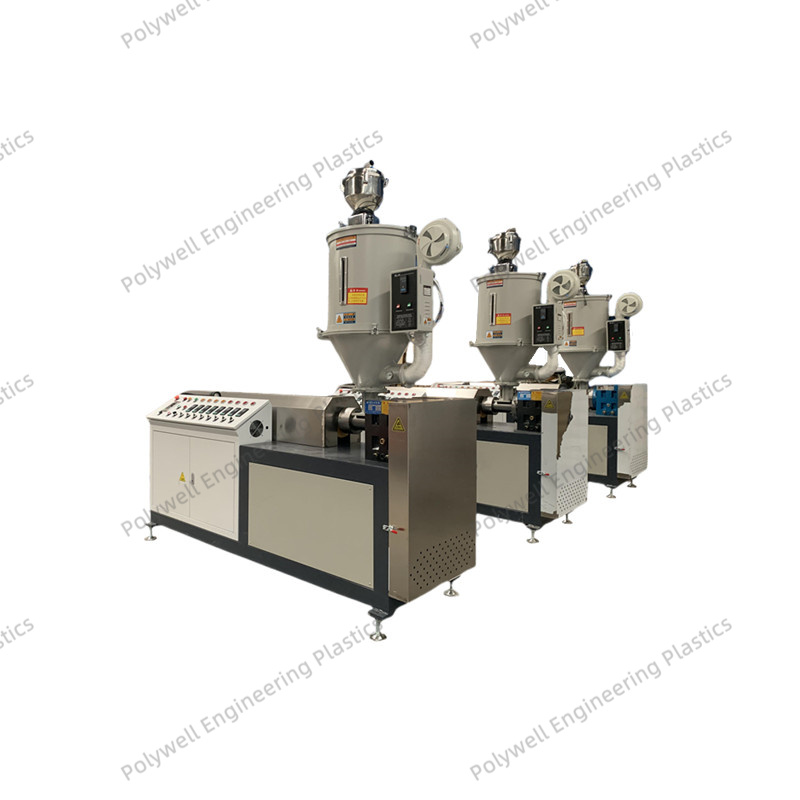
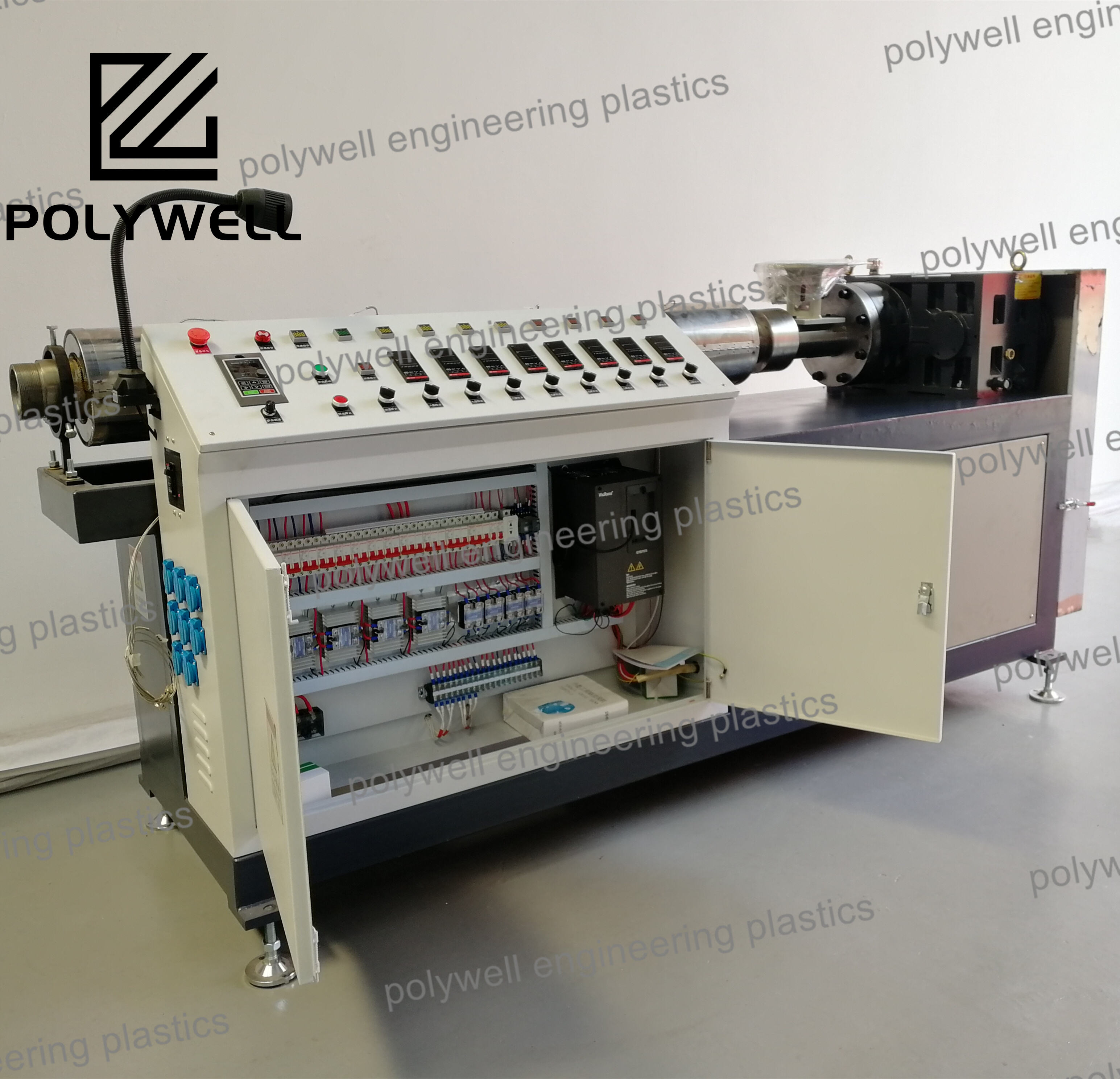
Vented single screw extruders, also known as two-stage extruders, represent advanced polymer processing equipment specifically designed for removing volatile components, moisture, or entrapped air during the extrusion process. These machines feature a distinctive screw design with two sequential sections separated by a vent zone where vacuum is applied. The first section performs conventional plasticating functions - feeding, compression, and melting - after which the melt enters a deep-channel decompression zone where volatiles flash off under vacuum. The second compression section then re-pressurizes the polymer for final discharge through the die. This configuration eliminates the need for pre-drying many hygroscopic materials like ABS, polycarbonate, or nylon, significantly reducing energy consumption and processing time. Vent port design is critical, typically employing specially engineered baffles to prevent melt ejection while maximizing surface area for volatile removal. Vacuum systems require careful sizing to handle the specific volatiles being removed, with condensation equipment often necessary to protect vacuum pumps. Processing parameters must be precisely balanced, particularly the fill level at the vent zone, which affects both devolatilization efficiency and stability. Screw designs incorporate specialized elements to renew the melt surface continuously, enhancing volatile removal through mechanisms such as blister rings, fluted sections, or torpedo elements. Applications extend beyond simple drying to include removal of polymerization solvents, residual monomers, plasticizer fumes, and process-generated gases. Modern vented extruders integrate sophisticated control systems that monitor vacuum levels, melt temperatures, and motor load to optimize devolatilization efficiency. While offering significant process advantages, these machines require more sophisticated operational expertise compared to conventional extruders, particularly regarding start-up procedures, material transition protocols, and maintenance of vacuum system components. The technology finds particular value in recycling operations where contaminant removal is essential, specialty compound production requiring precise volatile content control, and direct extrusion from reactor powders containing residual solvents.